Introduction
Pheromones, powerful chemical messengers that influence animal and human behavior, have long fascinated scientists. In contrast, pharmacology, the study of drugs and their interactions with the body, has revolutionized modern medicine. While both fields have distinct approaches, their convergence is unlocking exciting new possibilities in healthcare.

Pheromones: Nature’s Chemical Signals
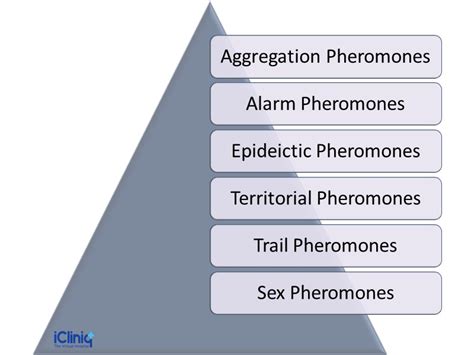
Pheromones are released by animals and humans, carrying information about identity, social status, and reproductive availability. They are detected by specialized receptors in the recipient, triggering behavioral and physiological responses.
Pharmacology: Targeting Specific Bodily Functions
Pharmacology focuses on developing and studying drugs that target specific receptors or enzymes in the body. These drugs can modulate biological processes, treating a wide range of diseases from infections to chronic conditions.
Pheromones vs. Pharmacology: Comparative Overview
| Feature | Pheromones | Pharmacology |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Natural, produced by organisms | Synthetic or natural, manufactured |
| Target | Receptors in the nose or skin | Receptors or enzymes throughout the body |
| Effect | Behavioral and social responses | Physiological and therapeutic effects |
| Specificity | Species- or sex-specific | Varies depending on the drug |
| Regulation | Limited | Stringently regulated by governing agencies |
Convergence and Innovation
Despite their differences, pheromones and pharmacology share a common goal: influencing biological functions. By combining their expertise, researchers are developing novel approaches that leverage the power of both fields.
Emerging Applications
1. Disease Diagnosis and Treatment: Pheromones can detect subtle changes in health, potentially aiding in early diagnosis and personalized treatments.
2. Mood and Behavior Regulation: Pheromone-based therapies have shown promise in improving mood, reducing anxiety, and enhancing social interactions.
3. Insect Control and Pest Management: Pheromones can disrupt insect mating or attract pests to traps, providing eco-friendly alternatives to pesticides.
4. Communication and Bonding: Synthetic pheromones could enhance social interactions, promote attachment, and improve communication.
5. Cancer Detection and Treatment: Pheromones released by cancer cells may provide a non-invasive method for early detection and targeted therapies.
Market Insights
The global pheromone market is projected to reach USD 3.2 billion by 2025, driven by advancements in research and applications in animal health, pest management, and human healthcare. Similarly, the global pharmacology market is expected to surpass USD 1.5 trillion by 2025, fueled by the development of new drugs and therapies.
Current Status and Future Directions
Current Status:
- Pheromone research is rapidly advancing, with new pheromones being identified and synthetically produced.
- Pharmacology continues to make significant contributions to disease management and drug development.
Future Directions:
- Collaborative research between pheromone and pharmacology scientists will unlock new insights and therapeutic applications.
- Ethical considerations and regulations will guide the safe and responsible use of pheromone-based interventions.
- Technological advancements will enhance our understanding of pheromone signaling and its potential applications.
Conclusion
The convergence of pheromone and pharmacology research is a game-changer in healthcare. By harnessing the power of both fields, we can unlock new avenues for disease diagnosis, treatment, and behavior modification. As research continues, the future of pheromone-based therapies and pharmacological interventions holds boundless possibilities.
FAQs
1. Are pheromones safe to use?
Pheromones are generally considered safe when used as intended. However, some synthetic pheromones may have potential side effects.
2. Can pheromones be used to attract mates?
Some pheromones have been shown to enhance attraction, but their effectiveness varies and is still under investigation.
3. Do pheromones work on humans?
Yes, humans have pheromone receptors and can respond to pheromones released by others.
4. What are the ethical implications of using pheromones?
Ethical considerations surround the potential manipulation of human behavior and the need for informed consent when using pheromones.
5. What are some promising areas for future research?
Exploring pheromones in personalized medicine, developing synthetic pheromone therapies, and investigating the role of pheromones in animal communication and environmental monitoring.
6. What are some challenges in pheromone-based applications?
Challenges include identifying and isolating specific pheromones, optimizing delivery methods, and ensuring regulatory compliance.