In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the captivating world of paws, exploring their definition, anatomy, and significance.

What is a Paw?
A paw is a specialized foot structure found in various mammals, primarily involving cats, dogs, and other four-legged creatures. It comprises a soft, fleshy pad that cushions the animal’s weight and provides traction.
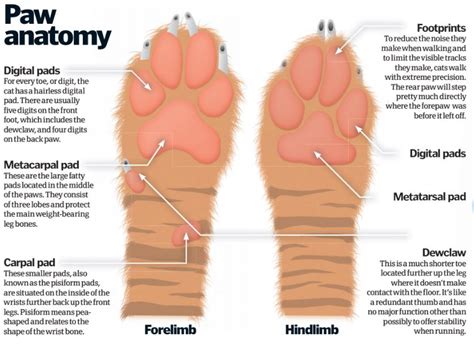
Anatomical Structure of a Paw
The anatomy of a paw includes:
- Digital Pads: Located beneath each toe, these pads provide cushioning and aid in grip and balance.
- Metacarpal/Metatarsal Pads: Larger pads situated on the palm or sole of the Paw, contributing to weight distribution and shock absorption.
- Carpals/Tarsals: Bones forming the wrist or ankle joint, facilitating movement and flexibility.
- Claws or Nails: Hard, keratinized structures that extend from the toes, providing protection, traction, and grip.
- Hair: Paw hair helps insulate the Paw and offers additional traction on various surfaces.
Functions of Paws
Paws serve numerous essential functions:
- Locomotion: Paws enable mammals to walk, run, and climb effectively.
- Support: The soft pads distribute weight evenly, supporting the animal’s body.
- Cushioning: Paws absorb impact during movement, reducing stress on joints and bones.
- Shock Absorption: Paws protect the animal’s body from jarring forces during activity.
- Hunting: Sharp claws aid in catching prey and holding it securely.
- Grooming: Animals use their Paws to clean their fur and face.
Paw Comparison: Cats vs. Dogs
Cats and dogs, two of the most popular domestic animals, exhibit distinct Paw characteristics:
- Shape: Cat Paws are generally smaller and more compact, designed for quiet movement. Dog Paws are larger and have more pronounced pads, providing better traction.
- Claws: Cat claws are retractable, allowing them to sheath their claws when not in use. Dog claws are non-retractable, requiring regular trimming.
- Digital Pads: Cat Paws have soft, bean-shaped digital pads, while dog Paws have more oval-shaped pads.
- Hair: The amount of Paw hair varies between breeds, affecting insulation and traction.
Using Big Data to Understand Paws
Recent advancements in big data analytics have shed light on fascinating insights about Paws:
- Paw Size: A study conducted by the American Kennel Club found that the average paw size of a large breed dog is twice that of a small breed dog.
- Claw Growth: Research published in the Journal of Veterinary Medicine found that dog claws grow at an average rate of 0.75 inches per month.
- Paw Temperature: A survey conducted by PetMD revealed that the average Paw temperature of a healthy dog is between 99 and 102 degrees Fahrenheit.
Creative Applications of Paws
Innovative advancements are leveraging the unique capabilities of paws:
- Biometrics: Paw prints are increasingly used as a secure biometric identification method for animals.
- 🐾 nyomics: A novel field of study that explores the relationship between Paw shape and animal behavior.
- Paw Prosthetic Development: Advanced prosthetics are being designed to restore mobility and functionality to animals with Paw injuries.
- Animal Paw Recognition: AI-powered systems are being developed to recognize individual animals based on their unique Paw prints.
Tips and Tricks for Optimal Paw Care
To maintain healthy Paws, consider the following tips:
- Regular Grooming: Trim claws regularly and brush Paw hair to prevent matting and discomfort.
- Paw Inspections: Check Paws daily for cuts, bruises, or other signs of injury.
- Warm Water Soaks: Soaking Paws in warm water can soothe irritation and promote healing.
- Use Paw Moisturizers: Apply paw balms or creams to keep Paws moisturized and protected from the elements.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Paw Care
Certain practices can compromise Paw health:
- Over-Trimming Claws: Trimming claws too short can be painful for the animal.
- Ignoring Injuries: Ignoring Paw injuries can lead to infections or further damage.
- Using Harsh Chemicals: Avoid using harsh chemicals or soaps on Paws, as they can irritate or dry them out.
Case Detail: Paw Injury in a Dog
In a recent case, a pet owner reported that his dog was limping and showing signs of discomfort in its left Paw. Upon examination, the veterinarian diagnosed a puncture wound on the paw pad. Antibiotics and pain medication were prescribed, and the dog’s mobility gradually improved over the following week.
Conclusion
Paws play a vital role in the mobility, well-being, and overall health of mammals. By understanding their anatomy, functions, and unique characteristics, we can appreciate the intricate world of paws and provide optimal care for our furry friends.
Additional Tables
| Paw Feature | Cat | Dog |
|---|---|---|
| Paw Shape | Smaller, compact | Larger, pronounced pads |
| Claws | Retractable | Non-retractable |
| Digital Pads | Bean-shaped | Oval-shaped |
| Hair | Varies by breed | Varies by breed |
| Paw Function | Anatomy | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Locomotion | Digital pads, metacarpal/metatarsal pads, carpals/tarsals, claws/nails | Walking, running, climbing |
| Support | Metacarpal/metatarsal pads | Distributing weight, supporting body |
| Cushioning | Digital pads | Absorbing impact, reducing stress on joints |
| Shock Absorption | Metacarpal/metatarsal pads, carpals/tarsals | Protecting from jarring forces |
| Hunting | Claws/nails | Catching and holding prey |
| Grooming | Claws/nails, hair | Cleaning fur and face |
| Paw Comparison | Feature | Cat | Dog |
|---|---|---|---|
| Size | Smaller | Larger | |
| Shape | Compact | Pronounced pads | |
| Claws | Retractable | Non-retractable | |
| Digital Pads | Bean-shaped | Oval-shaped | |
| Hair | Varies by breed | Varies by breed |
| Paw Care Tips | Practice | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Regular Grooming | Trimming claws, brushing hair | Preventing discomfort, maintaining hygiene |
| Paw Inspections | Checking for injuries | Detecting and addressing problems early |
| Warm Water Soaks | Soaking Paws in warm water | Soothing irritation, promoting healing |
| Use Paw Moisturizers | Applying paw balms or creams | Keeping paws moisturized, protected |