Introduction
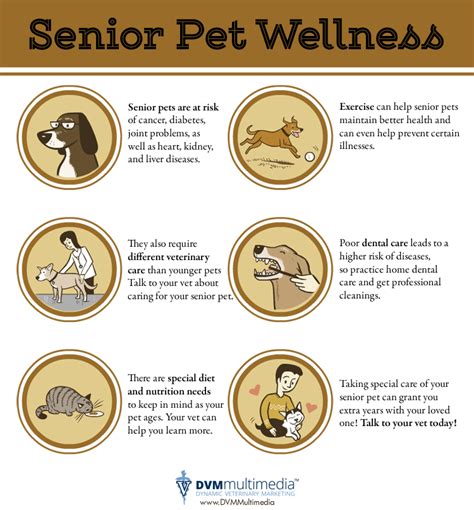
As our beloved pets reach their golden years, it’s crucial to provide them with specialized care and support. Notably, mammals face unique challenges in their later years that require specific attention. This article delves into the evolving landscape of mammalian care for senior pets, exploring cutting-edge advancements and providing practical tips to ensure their well-being and comfort.

Concerns and Considerations in Senior Mammals
As mammals age, they experience physical and cognitive changes that impact their overall health and well-being.
Physical Changes
- Reduced mobility: Joints and muscles weaken, leading to decreased activity levels and potential mobility issues.
- Dental problems: Dental disease is common in seniors, affecting oral hygiene and overall health.
- Sensory decline: Vision, hearing, and smell may deteriorate, impacting their daily life and interaction with their surroundings.
- Organ function: Kidney and liver function may decline, necessitating specialized diets and monitoring.
Cognitive Changes
- Cognitive impairment: Similar to humans, mammals can develop cognitive changes, including memory loss and confusion.
- Disorientation: They may become disoriented in familiar environments, requiring increased supervision and safety measures.
- Behavioral changes: Changes in behavior, such as aggression or anxiety, can occur due to cognitive decline or underlying medical conditions.
Mammaly Nutrition for Senior Pets
Appropriate nutrition plays a pivotal role in maintaining the health and well-being of senior mammals.
Nutritional Requirements
- Increased protein intake: Seniors require more protein to maintain muscle mass and support organ function.
- Reduced calories: Reduced activity levels demand lower calorie intake to prevent obesity.
- Specialized diets: Veterinary-recommended diets may be necessary for specific health conditions, such as kidney disease or dental problems.
Feeding Tips
- Avoid overfeeding: Senior mammals are prone to weight gain due to reduced activity levels.
- Use food puzzles: Encourage mental stimulation and slow down feeding to prevent overeating.
- Consider wet food: Wet food provides hydration and is easier for seniors with dental issues to consume.
Exercise and Physical Activity
Regular exercise is crucial for maintaining mobility and overall health in senior mammals.
Exercise Guidelines
- Gentle activities: Focus on low-impact activities, such as slow walks or swimming.
- Supervised playtime: Engage in interactive play sessions to stimulate their minds and bodies.
- Avoid intense exercise: Senior mammals may tire easily and should not be pushed beyond their limits.
Safety Considerations
- Prevent falls: Provide ramps or stairs to help seniors navigate safely.
- Use non-slip flooring: Ensure flooring is stable and does not pose a risk of falling.
- Avoid slippery surfaces: Wet surfaces can be hazardous for seniors with mobility issues.
Emotional and Behavioral Care
Providing a loving and supportive environment is essential for the emotional well-being of senior mammals.
Socialization and Interaction
- Regular interaction: Spend time with your senior pet daily, providing them with companionship and affection.
- Socialization: Facilitate gentle encounters with other animals or humans to prevent loneliness.
- Consider pet therapy: Pet therapy can provide emotional support and reduce stress levels.
Behavioral Changes
- Understanding behavior: Changes in behavior can be a sign of underlying medical conditions or cognitive decline.
- Patience and understanding: Be patient and understanding with behavioral changes, as they may struggle with confusion or anxiety.
- Professional help: If behavioral changes persist, consult with a veterinarian for further evaluation.
Health Care and Management
Regular veterinary checkups are essential for early detection and treatment of health issues in senior mammals.
Vet Visits and Screenings
- Regular checkups: Schedule semi-annual or annual checkups to monitor overall health and screen for underlying conditions.
- Diagnostic tests: Blood work, urine análisis, and imaging tests may be recommended to assess organ function and identify potential health problems.
- Vaccinations: Ensure senior pets are up-to-date on vaccinations to protect against preventable diseases.
Medications and Supplements
- Prescribed medications: Adhere to prescribed medication regimens for conditions such as arthritis, heart disease, or cognitive decline.
- Supplements: Discuss with your veterinarian whether supplementation, such as glucosamine or probiotics, may benefit your pet’s health.
End-of-Life Care
As senior pets approach the end of their lives, it’s important to provide compassionate and supportive end-of-life care.
- Quality of life: Focus on providing comfort and minimizing pain while maintaining a good quality of life.
- Hospice care: Consider hospice care to provide palliative support and pain management at home.
- End-of-life decisions: Consult with a veterinarian to discuss end-of-life options and make informed decisions based on your pet’s well-being.
Conclusion
Providing optimal care for senior mammals requires a comprehensive approach that encompasses medical, nutritional, emotional, and physical elements. By understanding the challenges they face and implementing appropriate care strategies, we can ensure that our beloved companions enjoy a comfortable and fulfilling later life. As the field of mammalian care for seniors continues to evolve, stay informed about advancements in diagnostics, treatments, and best practices to provide the best possible care for your precious pet.