Introduction
Mammals, including our beloved pets, exhibit a wide range of emotions, from happiness and love to fear and sadness. Over the years, scientists have made significant strides in understanding the emotional lives of these creatures, using a combination of behavioral observations, neuroimaging, and other techniques. However, much remains unknown about the emotional experiences of mammals.

Advances in Mammalian Emotion Research
1. Characterizing Emotions
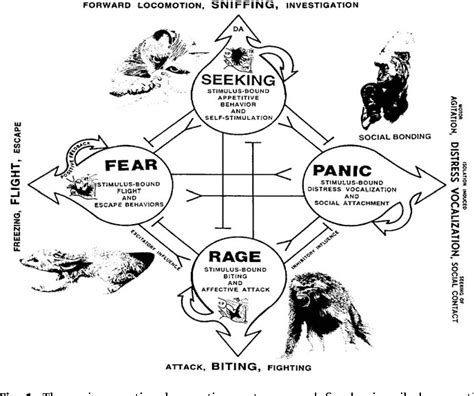
One of the key advances in mammalian emotion research has been the development of validated methods for characterizing emotions in animals. This includes observing physical behaviors, studying facial expressions, and measuring physiological responses. Researchers have also identified specific brain regions associated with different emotions, providing a neurobiological basis for understanding emotional states.
2. Understanding Emotional Intelligence
Another area of progress has been the study of emotional intelligence (EQ) in mammals. EQ refers to the ability to recognize and manage one’s own emotions, as well as the emotions of others. Researchers have found that mammals exhibit varying levels of EQ, with some species demonstrating remarkable abilities to understand and respond to emotional cues.
3. Measuring Emotional Well-being
Recent years have also seen the development of tools for measuring emotional well-being in mammals. These tools, such as the Animal Welfare Assessment Grid (AWAG) and the Compassionate Animal Care Index (CACI), provide a standardized way to assess emotions and identify animals that may be experiencing distress or discomfort.
Controversies in Mammalian Emotion Research
While significant progress has been made in understanding mammalian emotions, there remain several areas of controversy and debate.
1. Subjectivity of Emotional Interpretation
One of the challenges in studying mammalian emotions is the subjective nature of interpreting their behavior. For example, a dog wagging its tail may be expressing happiness or anxiety, depending on other contextual cues. Researchers must carefully consider multiple factors to accurately infer emotions in animals.
2. Anthropomorphism
Another concern is the potential for anthropomorphism, the attribution of human emotions to animals. While it is important to recognize the similarities between human and mammalian emotions, researchers must also be cautious not to overinterpret animal behavior based on their own subjective experiences.
Pet Emotions: A Unique Perspective
Pets hold a special place in our lives, and understanding their emotional experiences is crucial for their well-being. Research on pet emotions has focused on understanding how they express emotions, how they perceive human emotions, and how to promote their emotional health.
1. Emotional Expression in Pets
Pets communicate their emotions through various behaviors, including tail wagging, purring, barking, and meowing. By observing these behaviors and considering the context, we can gain insights into their emotional states.
2. Perception of Human Emotions
Pets are also remarkably adept at perceiving human emotions. They can recognize facial expressions, tone of voice, and body language, and they respond accordingly. Understanding this ability can enhance our interactions with pets and improve their emotional well-being.
3. Promoting Pet Emotional Health
Ensuring the emotional health of pets is essential for their overall well-being. This includes providing a safe and loving environment, meeting their physical and emotional needs, and seeking professional help if they exhibit signs of emotional distress.
Applications of Mammalian Emotion Research
The study of mammalian emotions has led to a wide range of applications, including:
1. Animal Welfare
Understanding emotions in animals is crucial for ensuring their welfare. By recognizing and addressing their emotional needs, we can create more humane living conditions and reduce stress and suffering.
2. Veterinary Medicine
Research on mammalian emotions can inform veterinary care, enabling practitioners to better diagnose and treat emotional disorders in animals.
3. Human-Animal Interactions
Understanding the emotional experiences of both humans and animals can enhance our interactions with our pets and other animals. This knowledge can lead to more compassionate and fulfilling relationships.
Future Directions
As research on mammalian emotions continues, several exciting areas of exploration await:
1. Refinement of Measurement Tools
Researchers are working to refine existing tools for measuring emotions in animals and develop new methods for assessing emotional states more effectively.
2. Cross-Species Comparisons
Comparative studies across different mammalian species can provide insights into the evolution of emotions and the commonalities and differences in emotional experiences.
3. Translational Applications
Translating emotion research into practical applications will improve the well-being of both animals and humans. This may include developing new therapies for animal emotional disorders and promoting empathy and compassion towards animals.
Conclusion
The study of mammalian and pet emotions is a rapidly evolving field that has profound implications for animal welfare, veterinary medicine, and human-animal interactions. By embracing a multifaceted approach that combines behavioral, neurobiological, and comparative research, we can gain a deeper understanding of these complex emotional worlds and improve the lives of both humans and animals in the years to come.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How can I tell if my pet is happy?
Look for signs such as a relaxed body posture, wagging tail (dogs), purring (cats), and a playful demeanor.
2. How can I promote my pet’s emotional health?
Provide a loving and supportive environment, meet their physical and emotional needs, and seek professional help if they exhibit signs of emotional distress.
3. How can I understand my pet’s emotions better?
Observe their behavior, consider the context, and learn about the species-specific ways they communicate emotions.