Introduction

With the world’s population projected to exceed 9 billion by 2050, the demand for food is expected to soar. Traditional agriculture practices, however, face numerous challenges, including climate change, land scarcity, and water pollution. Insect farming has emerged as a sustainable alternative, promising to meet the growing food demand while mitigating environmental impacts. However, the industry faces several challenges, particularly in the area of food safety.
Challenges in Insect Farming
- Scalability: Insect farming operations need to be scaled up to meet the growing demand for insect-based products. This requires substantial investment in infrastructure, technology, and expertise.
- Feedstock availability: Insects require a reliable and affordable source of feedstock, which can be challenging to secure in large quantities.
- Disease management: Insects are susceptible to various diseases that can decimate populations and impact yields. Effective disease management protocols are crucial to ensure the safety and sustainability of insect farming operations.
- Consumer acceptance: Although insect consumption is prevalent in many parts of the world, there is still some resistance in Western societies. Overcoming consumer reluctance and building trust in insect-based products is essential for the industry’s growth.
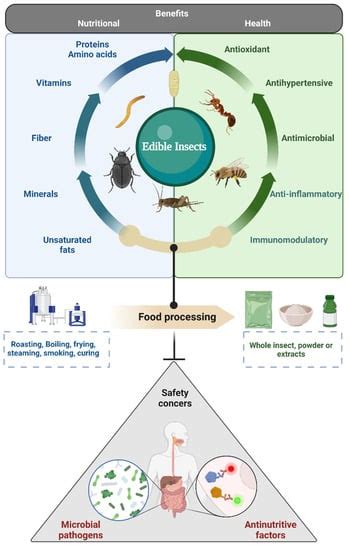
Food Safety Concerns
- Pathogens: Insects can harbor pathogenic microorganisms, such as Salmonella and E. coli, which can cause foodborne illnesses if consumed. Proper handling, storage, and processing are critical to prevent contamination.
- Heavy metals: Insects can accumulate heavy metals from their feedstock, potentially posing a health risk to consumers. Strict monitoring and quality control measures are necessary to ensure the safety of insect-based foods.
- Allergens: Some insects, such as crickets, are known allergens, and cross-contamination with other allergens can be a concern in insect farming operations.
- Novel foods: Insect-based foods are considered novel foods in many countries and require regulatory approval before they can be marketed. This can be a lengthy and costly process.
Strategies to Enhance Food Safety
- Good agricultural practices (GAPs): Establishing and adhering to GAPs throughout the insect farming process, from breeding to harvesting, is essential to minimize food safety risks.
- HACCP (Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points): Implementing a HACCP plan helps identify and control potential hazards at various stages of production.
- Traceability: Establishing a traceability system allows for the tracking of insects throughout the supply chain, making it easier to identify and recall contaminated products if necessary.
- Education and training: Providing comprehensive education and training to farmers and food handlers is crucial to ensure a high level of food safety awareness and compliance.
Potential of Insect Farming
Despite the challenges and food safety concerns, insect farming offers numerous potential benefits:
- Sustainable protein source: Insects are a rich source of protein, vitamins, and minerals, and can contribute to a more sustainable and nutritious food system.
- Reduced environmental impact: Insect farming has a lower environmental footprint compared to traditional livestock production, requiring less land, water, and feed.
- Waste management: Insects can be used to process organic waste, reducing the amount of waste sent to landfills or incinerated.
- Food security: Insect farming can increase food availability and stability, particularly in areas where traditional agriculture is constrained.
Conclusion
Insect farming holds immense promise as a sustainable and nutritious food source for the future. However, overcoming challenges in scalability, feedstock availability, disease management, and consumer acceptance is crucial. Ensuring food safety is paramount, and strategies such as GAPs, HACCP, traceability, and education are essential to mitigate potential risks. With continued investment in research, innovation, and regulation, the insect farming industry can play a significant role in meeting the growing food demand while promoting environmental sustainability.
Additional Information
Tables:
| Parameter | Insect Farming | Traditional Livestock |
|---|---|---|
| Greenhouse gas emissions | Lower | Higher |
| Water consumption | Lower | Higher |
| Land use | Lower | Higher |
| Feed conversion efficiency | Higher | Lower |
Pros and Cons of Insect Farming:
Pros:
- Sustainable and environmentally friendly
- High nutritional value
- Potential for waste management
- Can increase food availability
Cons:
- Scalability challenges
- Disease management concerns
- Consumer acceptance issues
- Novel food regulations
Highlight:
Insect farming can potentially revolutionize the global food system by providing a sustainable, nutritious, and environmentally friendly alternative to traditional livestock production.
Stand Out:
By addressing challenges in scalability, food safety, and consumer acceptance, the insect farming industry can unlock its full potential and become a major contributor to meeting the future food demand.