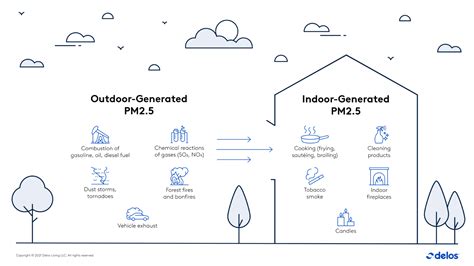
Introduction
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), indoor air pollution is one of the top ten global health risks, causing an estimated 4.3 million deaths each year. Poor indoor air quality (IAQ) can contribute to a range of respiratory problems, from mild irritation to serious illnesses such as asthma and lung cancer.

What Causes Poor Indoor Air Quality?
There are many factors that can contribute to poor IAQ, including:
- Tobacco smoke: Cigarette smoke contains over 7,000 chemicals, many of which are known carcinogens. Secondhand smoke exposure can cause a range of respiratory problems, including asthma, bronchitis, and lung cancer.
- Radon: Radon is a radioactive gas that can cause lung cancer. It is found in the soil and can enter homes through cracks in the foundation or basement.
- Volatile organic compounds (VOCs): VOCs are chemicals that are emitted from a variety of sources, including paint, cleaning products, and building materials. Some VOCs can cause respiratory irritation, headaches, and nausea.
- Dust mites: Dust mites are microscopic creatures that live in dust. They can trigger allergies and asthma attacks.
- Pets: Pet dander can trigger allergies and asthma attacks.
How Does Poor Indoor Air Quality Affect Respiratory Health?
Poor IAQ can irritate the airways and cause a range of respiratory problems, including:
- Asthma: Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disease of the airways. It can be triggered by a variety of factors, including poor IAQ.
- Bronchitis: Bronchitis is an inflammation of the bronchial tubes. It can be caused by a variety of factors, including poor IAQ.
- Emphysema: Emphysema is a chronic lung disease that causes damage to the alveoli, the tiny air sacs in the lungs. It can be caused by a variety of factors, including poor IAQ.
- Lung cancer: Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer death in the United States. It is caused by a variety of factors, including poor IAQ.
What Can Be Done to Improve Indoor Air Quality?
There are a number of things that can be done to improve IAQ, including:
- Ventilating your home: Opening windows and doors can help to ventilate your home and remove pollutants.
- Using an air purifier: Air purifiers can help to remove pollutants from the air.
- Avoiding smoking indoors: Smoking indoors can significantly increase the levels of pollutants in the air.
- Reducing the use of VOC-emitting products: VOCs can be emitted from a variety of sources, including paint, cleaning products, and building materials. Reducing the use of these products can help to improve IAQ.
- Controlling dust mites: Dust mites can be controlled by vacuuming frequently, using a damp cloth to wipe down surfaces, and encasing mattresses and pillows in dust mite covers.
- Keeping pets out of bedrooms: Pet dander can trigger allergies and asthma attacks. Keeping pets out of bedrooms can help to reduce exposure to pet dander.
Conclusion
Poor IAQ can have a significant impact on respiratory health. By taking steps to improve IAQ, you can reduce your risk of developing respiratory problems.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What are the most common causes of poor indoor air quality?
A: The most common causes of poor indoor air quality include tobacco smoke, radon, VOCs, dust mites, and pets.
Q: What are the health effects of poor indoor air quality?
A: Poor indoor air quality can cause a range of health effects, including respiratory irritation, allergies, asthma, and lung cancer.
Q: What can be done to improve indoor air quality?
A: There are a number of things that can be done to improve indoor air quality, including ventilating your home, using an air purifier, avoiding smoking indoors, reducing the use of VOC-emitting products, controlling dust mites, and keeping pets out of bedrooms.
Q: What are some tips for reducing exposure to tobacco smoke?
A: Some tips for reducing exposure to tobacco smoke include avoiding smoking indoors, asking smokers to smoke outside, and ventilating your home after someone has smoked indoors.
Q: What are some tips for reducing exposure to radon?
A: Some tips for reducing exposure to radon include sealing cracks in the foundation and basement, installing a radon mitigation system, and ventilating your home.
Q: What are some tips for reducing exposure to VOCs?
A: Some tips for reducing exposure to VOCs include using low-VOC products, ventilating your home after using VOC-emitting products, and avoiding spending extended periods of time in newly renovated or remodeled spaces.
Q: What are some tips for reducing exposure to dust mites?
A: Some tips for reducing exposure to dust mites include vacuuming frequently, using a damp cloth to wipe down surfaces, and encasing mattresses and pillows in dust mite covers.
Q: What are some tips for reducing exposure to pet dander?
A: Some tips for reducing exposure to pet dander include keeping pets out of bedrooms, bathing pets regularly, and using a HEPA filter in your vacuum cleaner.