Introduction
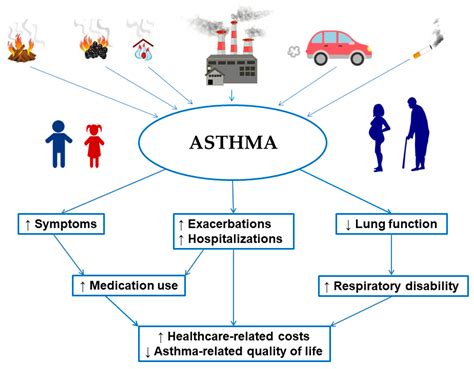
Asthma, a chronic respiratory condition, affects millions worldwide. While genetics plays a role, environmental factors, particularly indoor air quality (IAQ), significantly impact asthma development and exacerbation. This article delves into the crucial link between IAQ and asthma, exploring current insights, challenges, and strategies for improving IAQ to mitigate asthma symptoms.

Impact of Indoor Air Quality on Asthma
Indoor air can harbor various pollutants that trigger asthma symptoms:
- Particulate Matter (PM2.5): Fine particles from combustion sources, such as smoke and candles, can irritate the airways and worsen asthma.
- Allergens: Dust mites, pet dander, and pollen can trigger allergic reactions, which can lead to asthma attacks.
- Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs): Chemicals emitted from paints, cleaning products, and building materials can irritate the airways and trigger asthma.
- Secondhand Smoke: Exposure to tobacco smoke significantly increases the risk of asthma development and exacerbations.
Challenges in Maintaining Good Indoor Air Quality
Maintaining good IAQ can be challenging due to various factors:
- Lack of Ventilation: Modern homes and buildings are often sealed tightly for energy efficiency, reducing airflow and allowing pollutants to accumulate.
- Increased Use of Chemicals: The use of synthetic materials, cleaning products, and fragrances can release VOCs and other pollutants into the air.
- Pet Ownership: While pets can offer companionship, they can also contribute to allergens and dander in indoor environments.
- Outdoor Pollutants: Air pollution from traffic, industry, and wildfires can infiltrate buildings, affecting indoor air quality.
Improving Indoor Air Quality to Mitigate Asthma
Several strategies can improve IAQ and reduce asthma symptoms:
Ventilation and Filtration:
– Increase Ventilation: Open windows, use fans, or install mechanical ventilation systems to circulate fresh air and remove pollutants.
– Use Air Filters: HEPA filters can capture particulate matter and allergens, improving air quality.
Source Control:
– Eliminate Sources of Pollutants: Remove or reduce sources of VOCs, such as paints and cleaning products. Avoid smoking indoors.
– Control Allergens: Regularly clean surfaces, vacuum carpets and furniture, and use hypoallergenic bedding to reduce dust mites and pet dander.
Innovative Solutions for Enhanced IAQ
Emerging technologies offer innovative approaches to improve IAQ and mitigate asthma:
- Smart IAQ Monitors: Sensors can monitor indoor air quality in real-time, providing data on pollutants and triggering alerts when levels exceed recommended thresholds.
- Electrostatic Air Cleaners: These devices use electrostatic charges to attract and remove particulate matter and allergens from the air.
- Photocatalytic Oxidation (PCO): PCO systems use UV light and a catalyst to break down pollutants and VOCs, improving IAQ.
Key Findings from Research
- A study published in the journal “Environmental Health Perspectives” found that children living in homes with higher levels of PM2.5 had an increased risk of developing asthma.
- A study by the American Academy of Pediatrics showed that reducing exposure to secondhand smoke significantly reduced asthma symptoms and hospitalizations.
- A study in the journal “Allergy and Clinical Immunology” found that the use of HEPA filters in homes with dust mites reduced allergy symptoms and improved asthma control.
Conclusion
Indoor air quality plays a crucial role in asthma development and exacerbation. By understanding the impact of pollutants on asthma and implementing strategies to improve IAQ, we can significantly reduce asthma symptoms and improve the quality of life for millions. Continued research, innovation, and public health initiatives are essential to create healthier indoor environments and mitigate the burden of asthma.
FAQs
-
What are common symptoms of asthma triggered by poor IAQ?
– Wheezing, coughing, shortness of breath, chest tightness -
What are some tips for reducing allergens in homes with pets?
– Vacuum regularly, bathe pets, use HEPA filters, and keep pets out of bedrooms -
What technologies can help improve indoor air quality?
– Smart IAQ monitors, electrostatic air cleaners, PCO systems -
How does improving IAQ benefit people without asthma?
– Reduces respiratory irritation, improves sleep quality, and enhances overall health -
What are some government regulations related to IAQ and asthma?
– The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) sets standards for outdoor air quality, which can indirectly impact indoor air quality. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) regulates indoor air quality in workplaces. -
What are some ways to reduce VOCs indoors?
– Use low-VOC paints and cleaning products, ventilate during and after using potentially hazardous materials, and avoid using excessive fragrances. -
What is the role of healthcare professionals in improving IAQ for asthma patients?
– Healthcare professionals can advise patients on IAQ issues, recommend strategies for improving IAQ, and work with patients to develop personalized asthma management plans.