Introduction

As a responsible pet owner, making informed decisions about your dog’s health and well-being is paramount. Spaying and neutering, also known as sterilization, are crucial surgical procedures that offer numerous benefits for both your furry companion and your household. This comprehensive guide will delve into the essential aspects of dog spaying and neutering, exploring the pros and cons, discussing the optimal timing, and providing valuable insights into the latest trends and advancements in this veterinary field.
What’s the Difference Between Spaying and Neutering?
Spaying and neutering are surgical procedures that remove specific reproductive organs in dogs. Spaying, performed on female dogs, involves removing the ovaries and uterus, while neutering, performed on male dogs, involves removing the testicles. These procedures prevent unwanted pregnancies and eliminate the associated hormonal influences.
Why Spay or Neuter Your Dog?
Numerous compelling reasons support spaying and neutering your dog:
Health Benefits:
- Reduced Risk of Cancer: Spaying eliminates the risk of ovarian and uterine cancer in female dogs. Neutering reduces the risk of testicular cancer and prostate enlargement in male dogs.
- Prevention of Pyometra: Pyometra is a life-threatening uterine infection that can occur in unspayed female dogs. Spaying eliminates this risk.
- Improved Urinary Tract Health: Neutering can reduce the likelihood of urinary tract infections and incontinence in male dogs.
Behavioral Benefits:
- Curbed Aggression: Male dogs that are neutered tend to be less aggressive towards other dogs and people.
- Reduced Roaming and Escaping: Intact dogs are driven by the desire to find mates, which can lead to roaming and escaping behavior. Spaying and neutering eliminate this motivation.
- Improved Trainability: Sterilized dogs often display increased focus and obedience, making training easier.
Population Control:
- Prevention of Unwanted Litters: Spaying and neutering prevent unwanted pregnancies, contributing to the reduction of stray animal populations and the strain on animal shelters.
- Responsible Pet Ownership: Sterilizing your dog demonstrates responsible pet ownership and adherence to ethical breeding practices.
When to Spay or Neuter Your Dog?
The optimal timing for spaying and neutering varies depending on the individual dog and breed. General guidelines suggest:
- Female Dogs: 6-9 months of age, before their first heat cycle.
- Male Dogs: 6-9 months of age or when they reach sexual maturity.
Consult with your veterinarian to determine the best age for your specific dog.
How Much Does Spaying or Neutering Cost?
The cost of spaying or neutering can vary depending on the veterinarian, location, and the size and age of your dog. On average, spaying typically costs more than neutering. Expect to pay between $150-$500 for neutering and $200-$700 for spaying.
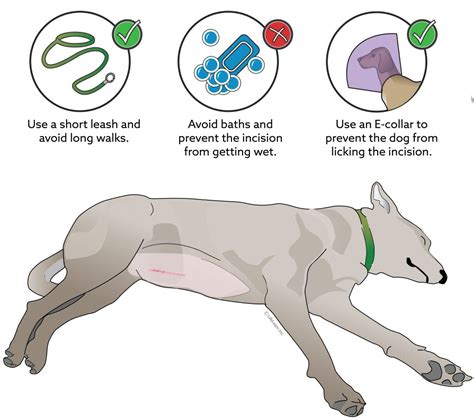
Recovery and Aftercare
After the surgery, your dog will require a short recovery period. Follow your veterinarian’s instructions carefully, which may include:
- Restricting activity
- Monitoring for excessive bleeding or swelling
- Keeping the incision site clean and dry
- Administering prescribed pain medication
Pros and Cons of Spaying and Neutering
Pros:
- Health benefits, including reduced cancer risk
- Behavioral improvements, such as curbed aggression
- Prevention of unwanted litters
- Responsible pet ownership
Cons:
- Surgical risks, although minimal
- Potential for weight gain, which can be managed with proper diet and exercise
- Possible urinary incontinence in female dogs, although rare
Alternatives to Spaying and Neutering
While spaying and neutering are highly recommended for most dogs, there may be certain circumstances where alternatives could be considered:
- Medical Conditions: Dogs with underlying health conditions that could be affected by surgery.
- Breeding: Dogs intended for responsible breeding programs may require alternative methods of birth control.
Consult with your veterinarian to explore these alternatives and determine the most appropriate option for your dog.
Future Trends and Advancements
The field of veterinary medicine is constantly evolving, and spaying and neutering are no exception. Researchers are exploring new techniques to improve the safety and efficacy of these procedures:
- Laparoscopic Spaying: A minimally invasive technique that uses a small camera and instruments to perform the surgery through small incisions.
- Non-Surgical Sterilization: Chemical sterilization methods that do not require surgery are under development.
These advancements aim to minimize surgical risks and enhance the overall well-being of our canine companions.
Case Studies
- Daisy, a 7-year-old female German Shepherd: Daisy experienced frequent urinary tract infections and exhibited aggressive behavior towards other dogs. After spaying, her urinary health improved significantly, and her aggression subsided, leading to a more harmonious household.
- Buddy, a 3-year-old male Labrador Retriever: Buddy struggled with constant roaming and escaping due to his desire to find mates. Neutering eliminated this behavior, making him a calmer and more obedient companion.
- Max, a 6-year-old male Rottweiler: Max was diagnosed with testicular cancer. Thanks to early neutering, the cancer was detected and treated promptly, increasing Max’s chances of survival and long-term health.
Conclusion
Spaying and neutering are essential procedures for the health, behavior, and well-being of dogs. While there are potential pros and cons to consider, the benefits far outweigh the risks for the vast majority of dogs. By understanding the importance of spaying and neutering, pet owners can make informed decisions that ensure a long, healthy, and happy life for their furry friends.
Additional Resources
- American Veterinary Medical Association: https://www.avma.org/resources-tools/pet-owners/petcare/spaying-and-neutering
- American Animal Hospital Association: https://www.aaha.org/pet-owner/article/spaying-and-neutering-your-pet-faq/
- Humane Society of the United States: https://www.humanesociety.org/resources/spaying-and-neutering-your-pet