As our beloved feline companions age, their unique health needs become paramount. Understanding the intricate changes that accompany seniorhood empowers us to provide optimal care and enhance their quality of life.

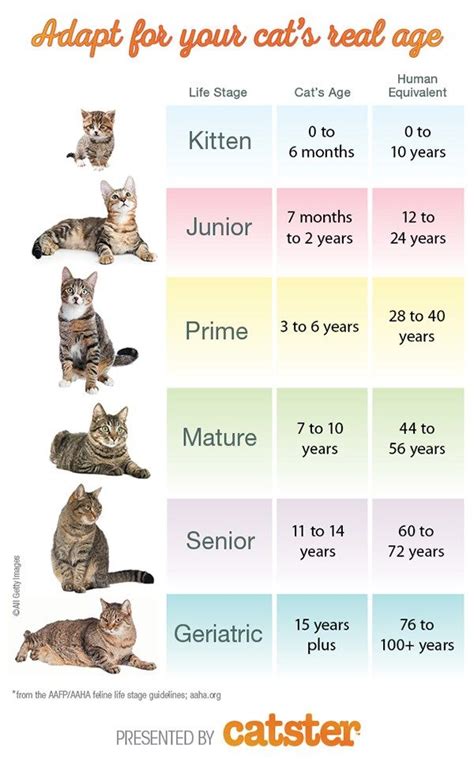
The Aging Cat: A Journey Through Time
7 years: Often considered the feline equivalent of human middle age, this milestone marks the onset of subtle physical and cognitive changes:
12-15 years: Senior Citizen Status: By this age, most cats are considered geriatric. Age-related health concerns become more pronounced, requiring increased veterinary attention.
20+: These extraordinary felines are considered耄耋之年. They may experience significant health challenges and require specialized care to maintain their well-being.
Common Health Concerns in Aging Cats
Musculoskeletal Issues:
Arthritis and joint pain: 1 in 4 cats over 6 years of age are affected by osteoarthritis.
Mobility issues: Stiffness and decreased range of motion can become apparent.
Dental Disease:
Periodontal disease: Affects 80% of cats by age 6.
Tooth loss: Can lead to malnutrition and infection.
Cognitive Dysfunction:
Feline cognitive dysfunction syndrome (CDS): Affects 28% of cats over 15 years of age.
Memory loss, disorientation, and changes in behavior.
Other Health Issues:
Heart disease
Kidney disease
Cancer
Hyperthyroidism
Obesity
Tailoring Care to the Aging Cat
Veterinary Care:
Regular checkups: Biannual checkups are crucial for early detection and management of health concerns.
Bloodwork and urinalysis: Monitor organ function and identify potential problems.
Vaccinations: Up-to-date vaccinations protect against preventable diseases.
Nutrition:
High-quality diet: Meets the senior cat’s nutritional needs.
Omega-3 fatty acids: Support joint health and cognitive function.
Reduced calories: Prevents obesity.
Exercise:
Regular exercise: Moderate activity helps maintain mobility and weight.
Interactive play: Stimulates mental and physical well-being.
Environment:
Safe and comfortable environment: Ramped litter boxes, non-slip flooring, and access to elevated surfaces.
Mental enrichment: Cat trees, scratching posts, and puzzle toys.
Home Care:
Grooming: Regular brushing removes loose hair and stimulates circulation.
Dental care: Daily tooth brushing prevents dental disease.
Nail clipping: Keeps nails trimmed to prevent scratching and injury.
Transitioning from Owner to Advocate
As caregivers, we play a pivotal role in our cats’ golden years. Embracing a proactive approach empowers us to:
Monitor Behavior: Observe any changes in appetite, grooming habits, or social interactions.
Seek Professional Advice: Consult with a veterinarian if concerned about any health issues.
Advocate for Comfort: Provide a comfortable and stress-free environment for our senior companion.
Celebrate the Journey: Cherish the twilight years and share every precious moment with love and gratitude.
Table 1: Common Health Concerns in Aging Cats
| Health Concern | Prevalence |
|---|---|
| Arthritis | 25% |
| Periodontal Disease | 80% |
| Feline Cognitive Dysfunction Syndrome | 28% |
| Heart Disease | 10-15% |
| Kidney Disease | 10-20% |
Table 2: Nutritional Guidelines for Aging Cats
| Nutrient | Recommended Amount |
|---|---|
| Protein | 30-50% |
| Fat | 10-20% |
| Carbohydrate | 30-40% |
| Omega-3 Fatty Acids | 500-1000 mg/day |
Table 3: Recommended Environmental Modifications for Aging Cats
| Modification | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Ramped Litter Boxes | Easier access for arthritic cats |
| Non-slip Flooring | Prevents falls and injuries |
| Elevated Surfaces | Provides a sense of security |
| Cat Trees | Encourages activity and mental stimulation |
Table 4: Home Care for Aging Cats
| Task | Frequency |
|---|---|
| Grooming | Daily |
| Dental Care | Daily |
| Nail Clipping | Monthly |
| Monitor Weight | Weekly |
Frequently Asked Questions
FAQs:
1. How often should I take my aging cat to the vet?
Regular checkups every 6 months are recommended.
2. What are the signs of arthritis in cats?
Limping, reluctance to move, and difficulty jumping.
3. How can I prevent dental disease in my senior cat?
Daily tooth brushing is essential.
4. What are the symptoms of feline cognitive dysfunction syndrome?
Memory loss, disorientation, and changes in behavior.
5. Is it normal for my aging cat to lose weight?
Unexplained weight loss can be a sign of an underlying health issue.
6. How can I make my home more comfortable for my aging cat?
Provide ramps, non-slip flooring, and access to elevated surfaces.
7. What is the average lifespan of a cat?
The average lifespan of an indoor cat is 15-20 years.
8. Are there any breed-specific health considerations for aging cats?
Certain breeds may be more prone to specific diseases, such as Maine Coons with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.
Conclusion
The journey through seniorhood is a natural part of the cat’s life cycle. By embracing a proactive approach, understanding the unique health needs of aging cats, and tailoring our care to their individual circumstances, we can empower our beloved companions to live longer, healthier, and more fulfilling lives.