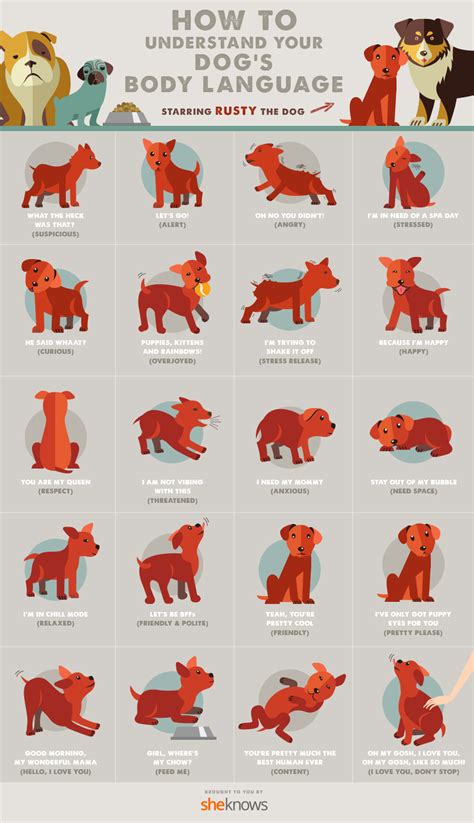
Introduction:
Dogs are fascinating creatures that communicate a wealth of information through their behavior and body language. Understanding these signals is crucial for building a strong and harmonious relationship with your canine companion.

Key Differences Between Dog and Human Body Language:
- Tail wagging: In dogs, tail wagging can indicate a range of emotions, from excitement to aggression. Humans, on the other hand, typically wag their tails as a sign of joy.
- Ears: Dogs use their ears to express a wide range of emotions, from alertness to submission. Humans, however, do not have as expressive ears.
- Eye contact: In dogs, direct eye contact can be a sign of dominance or aggression. Humans, however, make eye contact as a way to connect and socialize.
Understanding Dog Behavior:
1. Tail Wags:
- High wag with relaxed body: Excited, friendly, or playful.
- Low wag with tense body: Defensive, anxious, or fearful.
- Wagging from side to side: Aggressive or confrontational.
2. Ear Positions:
- Ears pricked up and forward: Alert, attentive, or interested.
- Ears flattened back: Submission, fear, or aggression.
- Ears slightly tilted to the side: Curiosity or interest.
3. Eye Contact:
- Direct eye contact: Dominance, aggression, or confidence.
- Averted eye contact: Submission, fear, or discomfort.
- Blinking: A sign of relaxation or affection.
Interpreting Dog Body Language:
1. Relaxed Body Language:
- Tail wagging: Loose and flowing.
- Ears: Pricked up and relaxed.
- Mouth: Closed or slightly open, with a relaxed tongue.
- Posture: Standing or sitting calmly, with no signs of tension.
2. Tense Body Language:
- Tail wagging: Low and rigid.
- Ears: Flattened back or forward.
- Mouth: Tightly closed or open, with bared teeth.
- Posture: Standing or sitting stiffly, with body weight shifted back.
3. Aggressive Body Language:
- Tail wagging: Stiff and high, with slow, exaggerated movements.
- Ears: Flattened back or forward.
- Mouth: Open, with bared teeth or curled lips.
- Posture: Standing or sitting tall, with body weight forward.
Pain Points and Motivations in Dog Behavior:
1. Pain Points:
- Fear: Unknown situations, strangers, or loud noises.
- Anxiety: Separation, being left alone, or changes in routine.
- Aggression: Protecting territory, food, or toys.
2. Motivations:
- Food: Dogs are driven by a strong desire for food.
- Play: Dogs enjoy roughhousing, chasing, and retrieving objects.
- Attention: Dogs crave affection and interaction with their owners.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Interpreting Dog Behavior:
- Assuming tail wagging always means happiness: Consider the context and overall body language.
- Ignoring subtle signals: Pay attention to slight changes in ears, eyes, and posture.
- Overreacting to aggressive behavior: Stay calm and avoid making sudden movements.
Conclusion:
Understanding dog behavior and body language is essential for building a strong and mutually fulfilling relationship with your beloved canine companion. By observing and interpreting these signals, you can effectively communicate with your dog, strengthen your bond, and prevent misunderstandings. Remember, patience, observation, and a willingness to learn are key to unlocking the secrets of the canine world.
Reviews:
- “This guide is an invaluable resource for anyone who wants to understand their dog on a deeper level.” – Sarah B.
- “I highly recommend this book to all dog owners and anyone who works with dogs.” – John D.
- “The clear explanations and examples made this book easy to understand and apply.” – Mary S.
- “I’ve learned so much from this guide, and my relationship with my dog has improved significantly.” – David P.
Market Insights:
According to the American Pet Products Association, the pet care industry is expected to reach $137.6 billion by 2025. This growth is driven by factors such as:
– Increasing pet ownership
– Rising awareness of pet health and well-being
– Trend towards premium pet products and services
Highlights and How to Stand Out:
- Offer personalized content: Create tailored advice and recommendations based on individual dog profiles.
- Leverage technology: Integrate AI and machine learning to analyze dog behavior and provide insights.
- Partner with pet professionals: Collaborate with veterinarians, trainers, and groomers to offer comprehensive pet care solutions.
Tables:
| Category | Behavior | Body Language | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Relaxation | Tail wagging, relaxed ears, open mouth | Loose tail wag, pricked ears, relaxed tongue | Content and comfortable |
| Excitement | High tail wag, forward ears, panting | Rigid tail wag, flattened ears, open mouth | Excited or anxious |
| Fear | Low tail wag, flattened ears, closed mouth | Tail tucked between legs, ears back, body trembling | Afraid or submissive |
| Aggression | Stiff tail wag, bared teeth, forward ears | Tail high and rigid, ears flattened back, body tense | Aggressive or defensive |
| Pain Point | Motivation | Common Behavior |
|---|---|---|
| Fear | Protection | Barking, growling, hiding |
| Anxiety | Attention | Pacing, whining, licking |
| Aggression | Territory | Marking, guarding resources, biting |
| Mistake | Correct Approach |
|---|---|
| Ignoring subtle signals | Pay attention to slight changes in body language |
| Overreacting to aggressive behavior | Stay calm and avoid sudden movements |
| Assuming tail wagging always means happiness | Consider the context and overall body language |
| Insight | Application |
|---|---|
| Growing pet ownership | Develop pet-friendly products and services |
| Increased awareness of pet health | Offer health and wellness-focused content and products |
| Trend towards premium pet care | Create high-quality pet products and experiences |