Understanding Dog Aggression

Dog aggression is a serious issue that can affect any breed of dog, regardless of its age, size, or temperament. It’s estimated that approximately 33% of dogs exhibit some form of aggression, with 10% of cases being classified as severe.
Causes of Dog Aggression
Numerous factors can contribute to dog aggression, making it a complex issue to address. Some of the most common causes include:
- Genetics: Certain breeds may be more prone to aggression, such as pit bulls, Rottweilers, and German Shepherds. However, genetics alone do not determine a dog’s aggression levels.
- Environment: Environmental factors, such as abuse, neglect, or isolation, can significantly increase the likelihood of aggression in dogs. Early socialization and positive training are crucial for preventing environmental triggers.
- Medical conditions: Pain, illness, or discomfort can trigger aggression in dogs. Therefore, ruling out any underlying medical conditions is essential when addressing aggression.
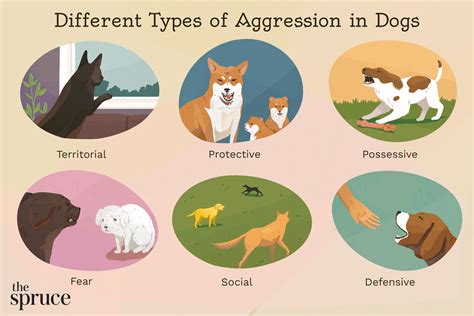
Types of Dog Aggression
Dog aggression can manifest in various forms, including:
- Dominance aggression: Dogs may become aggressive towards other animals or people they view as a threat to their dominance.
- Fear-based aggression: Dogs may become aggressive when they feel threatened or fearful, such as when cornered or exposed to unfamiliar situations.
- Protective aggression: Dogs may become aggressive to protect their owners, family, or territory from perceived threats.
- Predatory aggression: Some dogs may exhibit predatory aggression towards other animals, especially those smaller or weaker.
Training for Aggressive Dogs
While aggression in dogs can be a complex issue, it’s often manageable with the right training and intervention. Positive reinforcement and behavior modification techniques are essential for reducing aggressive behaviors.
Step-by-Step Approach to Training Aggressive Dogs
- Identify the root cause: Determine the specific triggers that lead to aggression and address them accordingly.
- Control the environment: Limit the dog’s exposure to known triggers while gradually introducing them in a controlled setting.
- Practice counter-conditioning: Pair the triggers with positive experiences, such as treats or praise, to change the dog’s emotional response.
- Use positive reinforcement: Reward desired behaviors, such as calm and non-aggressive responses, with treats or praise.
- Seek professional help: If the aggression is severe or unmanageable, consult a certified animal behaviorist or veterinary specialist for professional guidance and support.
Tips and Tricks for Training Aggressive Dogs
- Stay calm and confident during training sessions.
- Avoid physical punishment or harsh commands, as they can worsen aggression.
- Use treats and rewards to reinforce positive behaviors consistently.
- Be patient and persistent, as training takes time and effort.
- Seek support from experienced dog trainers or professionals when needed.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Training Aggressive Dogs
- Ignoring aggression or attributing it to dominance.
- Using physical punishment or harsh commands.
- Failing to identify and address underlying triggers.
- Not seeking professional help when aggression is severe or unmanageable.
- Relying solely on medication to control aggression without addressing behavioral issues.
Benefits of Training Aggressive Dogs
Training aggressive dogs provides numerous benefits, including:
- Enhancing the dog’s quality of life by reducing anxiety and aggression.
- Improving the safety of the dog and others around them.
- Strengthening the bond between the dog and its owner.
- Preventing further incidents and potential harm.
Prevention of Dog Aggression
Early Socialization and Training
Early socialization and training are crucial for preventing aggression in dogs. Exposing puppies to various people, animals, and environments helps them learn to interact appropriately. Obedience training teaches dogs basic commands and self-control, which can help prevent aggression in later life.
Responsible Ownership
Responsible ownership practices, such as providing proper exercise, nutrition, and healthcare, can help prevent aggression by addressing potential physical and emotional triggers. Spaying or neutering dogs can also reduce aggression related to reproductive instincts.
Monitoring for Signs of Aggression
Owners should be vigilant in monitoring their dogs for any signs of aggression, such as growling, snapping, or lunging. Early detection allows for prompt intervention and training to address underlying issues before they escalate into severe aggression.
ASPCA Statistics on Dog Aggression
The American Society for the Prevention of Cruelty to Animals (ASPCA) reports that:
- Dog bites account for approximately 1,300 emergency room visits annually.
- Children are the most likely victims of dog bites, with toddlers and infants being at the highest risk.
- The majority of dog bites occur in familiar settings, such as the victim’s home.
Conclusion
Dog aggression is a serious issue that requires a multi-faceted approach to address. Understanding the causes, types, and training methods for aggressive dogs is crucial. Early socialization and training, responsible ownership, and prevention strategies are essential for minimizing the risk of aggression and ensuring the safety and well-being of both dogs and the community. By working together with certified trainers, behaviorists, and veterinary professionals, we can create a world where dogs can live harmoniously and aggression is a thing of the past.