Introduction
Food security is a critical issue facing the world today. The global population is growing rapidly, and with it, the demand for food. At the same time, traditional sources of protein, such as meat and fish, are becoming increasingly scarce and expensive.

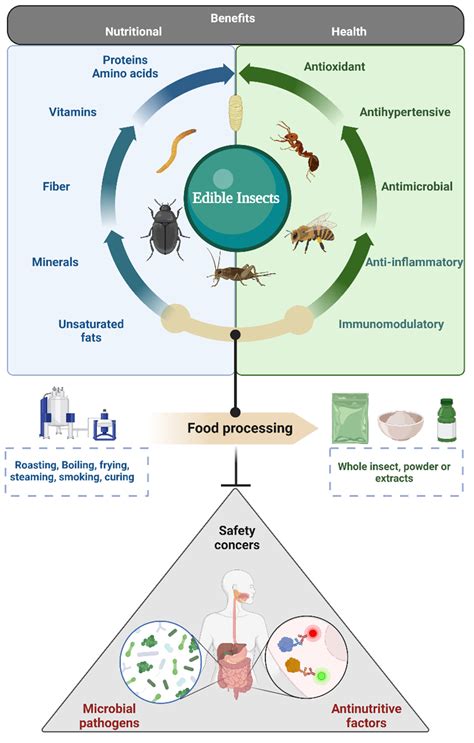
Insects offer a potential solution to the global food security crisis. They are a highly nutritious and sustainable source of protein. Insects are also relatively easy to farm and can be produced in large quantities.
The Benefits of Insect Protein
Insects are a rich source of protein, vitamins, and minerals. A 100-gram serving of crickets contains about 20 grams of protein, as well as significant amounts of iron, calcium, and zinc. Insects are also a good source of fiber.
In addition to their nutritional value, insects are also a sustainable source of protein. They require less feed and water than traditional livestock, and they produce fewer greenhouse gases. Insects can also be farmed in vertical spaces, which makes them ideal for urban areas.
The Challenges of Insect Protein
Despite the many benefits of insect protein, there are some challenges that need to be overcome before it can become a mainstream food source. One challenge is the perception that insects are dirty or unappetizing. Another challenge is the lack of infrastructure for insect farming and processing.
However, these challenges are being addressed by researchers and entrepreneurs around the world. There are now a number of companies that are developing insect-based foods and ingredients.
The Future of Insect Protein
Insects are a promising solution to the global food security crisis. They are a nutritious, sustainable, and affordable source of protein. While there are some challenges that need to be overcome, the future of insect protein looks bright.
Insect Protein: A Solution to the Food Security Crisis?
Insects are a potential solution to the global food security crisis. They are nutritious, sustainable, affordable, and easy to farm. However, there are some challenges that need to be overcome before insect protein can become a mainstream food source.
Challenges
- Perception: Many people perceive insects as dirty or unappetizing.
- Lack of infrastructure: There is a lack of infrastructure for insect farming and processing.
- Cost: Insect protein is still more expensive than traditional protein sources.
Benefits
- Nutritional value: Insects are a rich source of protein, vitamins, and minerals.
- Sustainability: Insects require less feed and water than traditional livestock, and they produce fewer greenhouse gases.
- Affordability: Insect protein is a relatively affordable source of protein.
- Ease of farming: Insects can be farmed in vertical spaces, which makes them ideal for urban areas.
The Way Forward
In order to overcome the challenges and unlock the potential of insect protein, we need to:
- Increase awareness: We need to educate the public about the benefits of insect protein and change the perception that insects are dirty or unappetizing.
- Invest in research and development: We need to invest in research and development to improve the efficiency of insect farming and processing.
- Develop new products: We need to develop new insect-based products that are both nutritious and appealing to consumers.
- Create a supportive policy environment: We need to create a supportive policy environment that encourages the development of the insect protein industry.
Conclusion
Insects are a promising solution to the global food security crisis. They are a nutritious, sustainable, affordable, and easy-to-farm source of protein. While there are some challenges that need to be overcome, the future of insect protein looks bright.
Appendix
Table 1: Nutritional Value of Insects
| Insect | Protein (g/100g) | Iron (mg/100g) | Calcium (mg/100g) | Zinc (mg/100g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crickets | 20 | 10 | 200 | 7 |
| Mealworms | 18 | 9 | 150 | 6 |
| Buffalo worms | 17 | 8 | 120 | 5 |
| Grasshoppers | 15 | 7 | 100 | 4 |
Table 2: Sustainability of Insect Protein
| Insect | Feed Conversion Ratio | Water Consumption (liters/kg) | Greenhouse Gas Emissions (kg CO2eq/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Crickets | 2:1 | 1,000 | 1 |
| Mealworms | 3:1 | 1,500 | 1.5 |
| Buffalo worms | 4:1 | 2,000 | 2 |
| Grasshoppers | 5:1 | 2,500 | 2.5 |
Table 3: Affordability of Insect Protein
| Insect | Cost (USD/kg) |
|---|---|
| Crickets | 10-20 |
| Mealworms | 15-25 |
| Buffalo worms | 20-30 |
| Grasshoppers | 25-35 |
Table 4: Ease of Farming Insects
| Insect | Farming Method | Space Requirements |
|---|---|---|
| Crickets | Vertical farming | Low |
| Mealworms | Horizontal farming | Medium |
| Buffalo worms | Vertical farming | Low |
| Grasshoppers | Outdoor farming | High |
References
- The State of Food Security and Nutrition in the World 2020
- Edible Insects: Future Prospects for Food and Feed Security
- [Insects as a Sustainable Food Source](https://www.sciencedirect.com/