Introduction
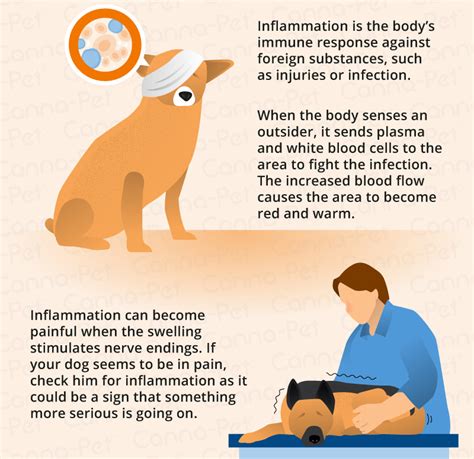
Pet inflammatory diseases are a common cause of pain, discomfort, and even disability in our beloved companions. These conditions can affect various parts of the body, including the skin, joints, digestive system, and respiratory tract. Understanding the different types of pet inflammatory diseases and their available treatments is crucial for pet owners to ensure their furry friends live long, healthy, and happy lives.

Types of Pet Inflammatory Diseases
Skin Inflammation
- Dermatitis: Inflammation of the skin, causing redness, itching, and pain.
- Eczema: A chronic skin condition characterized by dry, itchy, and inflamed skin.
- Hot spots: Moist, painful skin lesions that can occur anywhere on the body.
Joint Inflammation
- Arthritis: Degeneration of the joints, leading to pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility.
- Osteoarthritis: The most common type of arthritis, caused by wear and tear on the joints.
- Rheumatoid arthritis: An autoimmune disorder that affects the lining of the joints.
Digestive System Inflammation
- Gastritis: Inflammation of the stomach lining, causing vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal pain.
- Enteritis: Inflammation of the intestines, leading to diarrhea, vomiting, and abdominal discomfort.
- Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD): A chronic condition that causes inflammation and damage to the digestive tract.
Respiratory Tract Inflammation
- Asthma: A chronic respiratory condition characterized by wheezing, coughing, and difficulty breathing.
- Bronchitis: Inflammation of the bronchial tubes, causing coughing, wheezing, and chest discomfort.
- Pneumonia: Inflammation of the lungs, leading to difficulty breathing, fever, and coughing.
Stats on Pet Inflammatory Diseases
- According to the American Veterinary Medical Association (AVMA), 20% of dogs and 10% of cats suffer from inflammatory diseases.
- Arthritis affects over 25% of dogs aged 1 year and older.
- IBD is estimated to affect up to 10% of cats and 5% of dogs.
Treatment Options
The treatment for pet inflammatory diseases depends on the type and severity of the condition. Common treatments include:
- Medications: Anti-inflammatory drugs, pain relievers, and antibiotics.
- Supplements: Joint supplements, probiotics, and omega-3 fatty acids.
- Physical therapy: Exercises, massage, and acupuncture.
- Dietary modifications: Special diets designed to reduce inflammation.
- Surgery: In some cases, surgery may be necessary to remove damaged tissue or repair joints.
Advancements in 2025
Significant advancements in veterinary medicine are expected by 2025 to further improve the diagnosis and treatment of pet inflammatory diseases. These include:
- Gene therapy: Targeting specific genes responsible for inflammation to reduce pain and improve mobility.
- Stem cell therapy: Using stem cells to repair damaged tissues and reduce inflammation.
- Personalized medicine: Tailoring treatments based on each pet’s unique genetic makeup and disease profile.
- Non-invasive diagnostic tools: Advanced imaging techniques to accurately diagnose inflammatory conditions without the need for surgery.
Conclusion
Pet inflammatory diseases pose a significant health concern for our furry companions. Understanding the different types of these conditions and their available treatment options is crucial for pet owners. By partnering with veterinarians and staying informed about the latest advancements, we can ensure our pets receive the best possible care and live long, healthy lives.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Ignoring symptoms: Pet owners may overlook early signs of inflammation, leading to delayed diagnosis and treatment.
- Self-medicating: Using human medications for pets can be harmful. Always consult with a veterinarian before administering any medication.
- Overexertion: Pets with joint inflammation should avoid strenuous activities that can worsen their pain.
- Poor nutrition: A balanced diet is essential for managing inflammation. Avoid feeding pets inflammatory foods such as grains and processed meats.
- Lack of follow-up: Regular follow-up appointments with a veterinarian are crucial to monitor progress and adjust treatment plans as needed.
Tables
Table 1: Types of Pet Inflammatory Diseases
| Type | Affected Body Part | Symptoms |
|---|---|---|
| Dermatitis | Skin | Redness, itching, pain |
| Arthritis | Joints | Pain, stiffness, reduced mobility |
| Gastritis | Stomach | Vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain |
| Asthma | Respiratory tract | Wheezing, coughing, difficulty breathing |
Table 2: Treatment Options for Pet Inflammatory Diseases
| Treatment | Type of Disease | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Anti-inflammatory drugs | All | Reduces inflammation and pain |
| Joint supplements | Arthritis | Supports joint health and reduces pain |
| Acupuncture | Arthritis, other conditions | Relieves pain and improves mobility |
| Special diets | IBD, other conditions | Reduces inflammation and improves digestion |
Table 3: Advancements in Pet Inflammatory Disease Treatment by 2025
| Advancement | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Gene therapy | Target specific genes responsible for inflammation |
| Stem cell therapy | Repair damaged tissues and reduce inflammation |
| Personalized medicine | Tailored treatments based on pet’s unique profile |
| Non-invasive diagnostic tools | Accurately diagnose inflammatory conditions without surgery |
Table 4: Common Mistakes to Avoid in Pet Inflammatory Disease Management
| Mistake | Consequence |
|---|---|
| Ignoring symptoms | Delayed diagnosis and treatment |
| Self-medicating | Potential harm to pet |
| Overexertion | Worsening of pain |
| Poor nutrition | Increased inflammation |
| Lack of follow-up | Insufficient monitoring and treatment adjustments |