Introduction
Vaccinations are an essential part of keeping your dog healthy and protected from potentially fatal diseases. Knowing when and which vaccinations your dog needs can be confusing, especially with the ever-changing landscape of veterinary medicine. In this comprehensive guide, we will provide you with the most up-to-date information on the core and non-core vaccinations recommended for dogs in 2025.

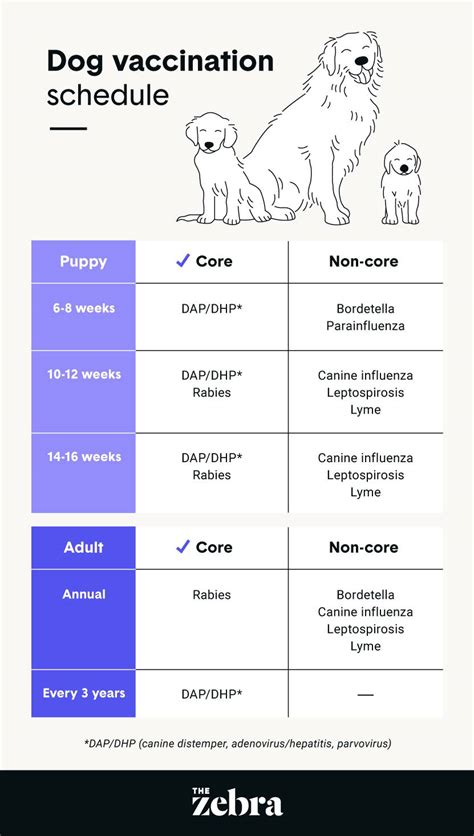
Core Vaccinations for Puppies
Core vaccinations are considered essential for all dogs, regardless of their lifestyle or risk factors. They protect against highly contagious and potentially deadly diseases that are commonly found in dogs. The core vaccines for puppies typically include:
| Vaccination | Age at First Dose | Subsequent Doses |
|---|---|---|
| Canine Distemper Virus (CDV) | 6-8 weeks | 12-16 weeks, 16-20 weeks |
| Canine Parvovirus (CPV) | 6-8 weeks | 12-16 weeks, 16-20 weeks |
| Canine Adenovirus-2 (CAV-2) | 6-8 weeks | 12-16 weeks, 16-20 weeks |
| Rabies Virus | 12-16 weeks | Annual boosters thereafter |
Non-Core Vaccinations for Dogs
Non-core vaccinations are recommended for dogs based on their individual lifestyle and risk factors. They protect against less common diseases that may be more prevalent in certain areas or among certain breeds. Common non-core vaccines include:
| Vaccination | Recommended for Dogs At Risk Of |
|---|---|
| Canine Parainfluenza Virus (CPi) | Dogs in kennels or boarding facilities |
| Canine Bordetella Bronchiseptica | Dogs in kennels or boarding facilities |
| Canine Influenza Virus (CIV) | Dogs in high-traffic areas or those that travel frequently |
| Lyme Disease Vaccine | Dogs living in areas with a high prevalence of Lyme disease |
| Leptospirosis Vaccine | Dogs living in areas with standing water or exposure to wildlife |
Vaccination Schedule for Adult Dogs
After puppies have received their initial series of core vaccinations, they will need annual boosters to maintain immunity. The following table outlines the recommended vaccination schedule for adult dogs:
| Vaccination | Annual Booster |
|---|---|
| Canine Distemper Virus (CDV) | Yes |
| Canine Parvovirus (CPV) | Yes |
| Canine Adenovirus-2 (CAV-2) | Yes |
| Rabies Virus | Yes |
| Canine Parainfluenza Virus (CPi) | As needed, based on risk |
| Canine Bordetella Bronchiseptica | As needed, based on risk |
| Canine Influenza Virus (CIV) | As needed, based on risk |
| Lyme Disease Vaccine | As needed, based on risk |
| Leptospirosis Vaccine | As needed, based on risk |
Benefits of Vaccinating Your Dog
Vaccinating your dog offers numerous benefits, including:
- Protection against deadly diseases: Vaccinations can significantly reduce the risk of your dog contracting serious and potentially fatal diseases.
- Improved health outcomes: Dogs that are vaccinated are less likely to develop severe symptoms or complications if they do become infected.
- Lower veterinary costs: Vaccinations can help prevent expensive treatments and hospitalizations for diseases that can be avoided.
Importance of Following the Vaccination Schedule
It is crucial to follow the recommended vaccination schedule for your dog to ensure optimal protection. Skipping or delaying vaccinations can put your dog at risk of contracting preventable diseases.
Considerations for High-Risk Dogs
Some dogs have a higher risk of exposure to certain diseases due to their lifestyle or breed. These dogs may require more frequent vaccinations or additional non-core vaccines. It is important to discuss your dog’s individual needs with your veterinarian.
Future Trends in Dog Vaccinations
Veterinary research is constantly evolving, leading to advancements in vaccine technology. In the future, we can expect to see:
- Improved vaccine efficacy: New vaccines may provide longer-lasting protection and reduce the need for frequent boosters.
- Combination vaccines: Vaccines that protect against multiple diseases in a single shot can simplify the vaccination process and reduce the number of injections your dog receives.
- Tailored vaccines: Personalized vaccines may be developed based on a dog’s individual risk factors and genetic makeup.
Conclusion
Dog vaccination schedules are essential for maintaining the health and well-being of our furry companions. By following the recommended schedule and consulting with your veterinarian, you can ensure that your dog is protected against preventable diseases. Remember, vaccination is a key part of responsible pet ownership.