Importance of Cat Vaccinations
Vaccinations are crucial for protecting cats from various life-threatening diseases. According to the American Veterinary Medical Association (AVMA), “Vaccinations are one of the most important things you can do to keep your cat healthy and safe.” They prevent the spread of contagious illnesses, reduce the severity of symptoms, and in some cases, even save lives.

Core Vaccinations
Core vaccinations are essential for all cats and are typically recommended by veterinarians. These vaccinations protect against diseases that are highly contagious and can be fatal.
Feline Viral Rhinotracheitis (FVR)
- Vaccine: FVR or FVRCP
- Protection: Respiratory infection, conjunctivitis, stomatitis, and pneumonia
- Recommended Frequency: Every 1-3 years
Feline Calicivirus (FCV)
- Vaccine: FCV or FVRCP
- Protection: Nasal discharge, sneezing, conjunctivitis, stomatitis, and pneumonia
- Recommended Frequency: Every 1-3 years
Feline Panleukopenia (FPV)
- Vaccine: FPV or FVRCP
- Protection: Fatal intestinal infection
- Recommended Frequency: Every 3 years
Rabies
- Vaccine: Rabies
- Protection: Fatal neurological disease
- Recommended Frequency: As required by law, typically every 1-3 years
Non-Core Vaccinations
Non-core vaccinations are recommended for cats based on their lifestyle, exposure risks, and geographical location.
Feline Leukemia Virus (FeLV)
- Vaccine: FeLV
- Protection: Cancer and immunosuppression
- Recommended Frequency: Every 1-3 years for high-risk cats (e.g., outdoor cats)
Feline Immunodeficiency Virus (FIV)
- Vaccine: FIV
- Protection: Immunosuppression and increased susceptibility to infections
- Recommended Frequency: Every 1-2 years for high-risk cats (e.g., cats in catteries)
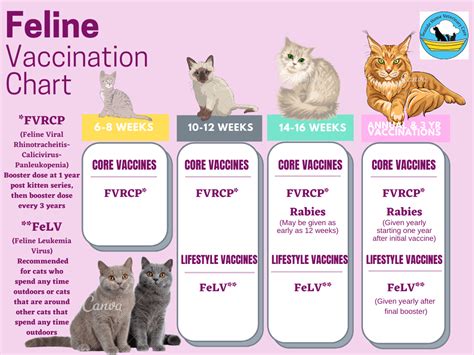
Vaccination Schedules
Kittens
- 6-8 weeks: FVRCP-P (first dose)
- 10-12 weeks: FVRCP-P (second dose)
- 14-16 weeks: FVRCP-P (third dose), rabies (first dose)
- 12 months: Rabies (booster)
Adult Cats
- Annually: FVRCP, rabies
- Every 3 years: FPV (booster)
- As needed: Non-core vaccinations (e.g., FeLV, FIV)
Vaccination Requirements
Vaccination requirements may vary depending on local laws and regulations. However, rabies vaccination is typically legally required in most areas. It is important to check with your local veterinarian or animal control agency for specific requirements.
Vaccination Considerations
Side Effects
Vaccinations can sometimes cause mild side effects, such as lethargy, injection site soreness, or a temporary decrease in appetite. These side effects usually subside within a few days and are not a cause for concern.
Allergies
Some cats can be allergic to vaccines. If your cat experiences an allergic reaction (e.g., swelling, hives, difficulty breathing), seek veterinary attention immediately.
Immunocompromised Cats
Cats with compromised immune systems may not respond as well to vaccinations. Consult with your veterinarian to determine the best vaccination schedule and precautions for your cat.
Vaccination Costs
The cost of vaccinations can vary depending on the type of vaccine, the frequency of administration, and the veterinarian’s fees. Typically, core vaccines are less expensive than non-core vaccines.
Conclusion
Vaccinations are essential for protecting cats from infectious diseases. By following recommended vaccination schedules and requirements, you can help keep your feline companion healthy and happy for years to come.