Introduction
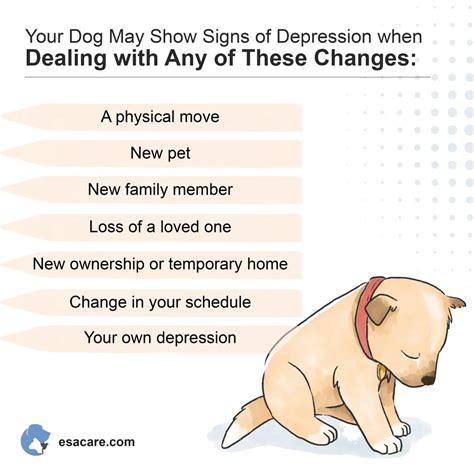
In the face of rising mental health challenges, the power of companion animals has emerged as a beacon of hope. Dogs, in particular, have proven to be exceptional therapists, offering unconditional love, companionship, and routine to individuals struggling with depression. This comprehensive guide explores the transformative role of dog parenting in managing and overcoming depression, providing invaluable information for those seeking solace through canine connection.

The Link Between Dog Parenting and Depression
Research consistently demonstrates the profound impact of dog ownership on mental well-being. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), pet owners are 40% less likely to experience depression than non-pet owners. The American Heart Association reports that dog owners have a 24% lower risk of developing depression.
How Dogs Help:
- Unconditional Love: Dogs provide a constant source of affection, acceptance, and joy, unconditionally offering comfort and reducing feelings of loneliness and isolation.
- Increased Physical Activity: Dogs encourage daily walks, runs, and playtime, which release endorphins that have mood-boosting effects.
- Structure and Routine: Dogs require regular feeding, grooming, and walks, providing a sense of structure and purpose that can reduce stress and anxiety.
- Social Interaction: Dogs facilitate social interactions between their owners and others, fostering a sense of belonging and reducing feelings of isolation.
Benefits of Dog Parenting for Depression
Research has conclusively established the myriad benefits of dog parenting for individuals with depression:
- Reduced Symptoms: Dog ownership is associated with decreased symptoms of depression, including reduced feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and worthlessness.
- Improved Mood: Dogs provide a natural mood boost, releasing feel-good hormones like serotonin and dopamine.
- Increased Self-Esteem: Caring for a dog can foster feelings of accomplishment, responsibility, and self-worth, which can enhance self-esteem.
- Reduced Stress: Dogs offer a calming effect, reducing stress levels and promoting relaxation.
- Enhanced Sleep: Dogs can help regulate sleep patterns, reducing the insomnia commonly associated with depression.
Choosing the Right Dog
Selecting the right dog breed is crucial for success in dog parenting for depression. Consider the following factors:
- Personality: Opt for a breed with a calm and affectionate temperament, such as Golden Retrievers, Labrador Retrievers, and Poodles.
- Energy Level: Match the dog’s energy level to your own, considering factors like age, activity level, and lifestyle.
- Size: Ensure the dog’s size is appropriate for your living space and lifestyle.
- Allergies: If allergies are a concern, explore hypoallergenic breeds like Bichons Frises and Maltese.
- Special Needs: Consider adopting a dog with special needs, such as a senior dog or one with a disability. This can provide both companionship and a sense of purpose.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Expecting too Much: Dogs cannot replace professional therapy, medication, or other forms of treatment for depression.
- Overwhelming Yourself: Start with a low-energy dog breed and gradually increase the level of care as you feel more capable.
- Failing to Provide Enrichment: Avoid leaving your dog alone for extended periods, and provide plenty of toys, activities, and attention.
- Neglecting Your Own Health: Prioritize your own physical and mental health alongside caring for your dog.
- Feeling Guilty: Recognize that caring for a dog may have its challenges, and don’t feel guilty if you need to take breaks or ask for help.
FAQs
1. Are there any risks to dog parenting for depression?
There are potential risks, such as financial expenses, time commitment, and the possibility of aggression or destructive behavior. However, with careful planning and training, these risks can be minimized.
2. How much time do I need to commit to dog parenting?
Depending on the dog’s breed and age, expect to spend several hours each day on walking, feeding, grooming, and training.
3. What if I can’t afford a dog?
Consider volunteering at a local animal shelter or dog park, or fostering a dog temporarily. These options can provide companionship and the benefits of dog parenting without the financial burden.
4. How do I handle setbacks or difficulties in dog parenting?
Seek support from a veterinarian, animal behaviorist, or mental health professional. Remember that setbacks are normal and don’t let them discourage you.
5. What if my dog becomes a trigger for my depression?
If caring for your dog exacerbates your depression, consider re-evaluating the situation and seeking professional help.
6. How can I ensure my dog’s well-being while managing my own depression?
Prioritize your dog’s needs, but don’t neglect your own health. Set boundaries, delegate tasks to family or friends when possible, and seek support if needed.
Conclusion
Dog parenting can be a transformative journey for individuals struggling with depression. By providing unconditional love, companionship, and routine, dogs offer a path toward recovery and enhanced well-being. With careful planning and a commitment to both your own health and your dog’s needs, you can harness the power of the human-animal bond to overcome the challenges of depression.
Additional Resources:
Tables
Table 1: Benefits of Dog Parenting for Depression
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Reduced Symptoms | Decreased sadness, hopelessness, and worthlessness |
| Improved Mood | Release of endorphins and dopamine |
| Increased Self-Esteem | Fosters feelings of accomplishment and responsibility |
| Reduced Stress | Calming effect, reducing stress levels |
| Enhanced Sleep | Regulate sleep patterns, reducing insomnia |
Table 2: Common Dog Breeds for Depression Support
| Breed | Temperament | Energy Level |
|---|---|---|
| Golden Retriever | Friendly, affectionate, and playful | Moderate |
| Labrador Retriever | Gentle, loyal, and outgoing | High |
| Poodle | Intelligent, hypoallergenic, and social | Moderate to high |
| Bichon Frise | Cheerful, affectionate, and hypoallergenic | Low to moderate |
| Maltese | Gentle, cuddly, and hypoallergenic | Low |
Table 3: Common Mistakes in Dog Parenting for Depression
| Mistake | Description |
|---|---|
| Expecting too Much | Relying solely on dogs to cure depression |
| Overwhelming Yourself | Starting with a high-maintenance dog |
| Failing to Provide Enrichment | Leaving dogs alone for extended periods |
| Neglecting Your Own Health | Prioritizing dog care over your own well-being |
| Feeling Guilty | Feeling responsible for all of the dog’s needs |
Table 4: FAQs and Answers on Dog Parenting for Depression
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| Are there any risks to dog parenting for depression? | Yes, potential risks include financial expenses, time commitment, and aggressive behavior |
| How much time do I need to commit to dog parenting? | Several hours each day, depending on the dog’s breed and age |
| What if I can’t afford a dog? | Consider volunteering or fostering instead |
| How do I handle setbacks or difficulties in dog parenting? | Seek support from professionals and remember that setbacks are normal |
| What if my dog becomes a trigger for my depression? | Re-evaluate the situation and seek professional help |