Introduction
The health and well-being of our beloved pets are paramount, and nutrition plays a pivotal role in maintaining their optimal well-being. In recent years, research has shed light on the intricate relationship between pet nutrition and gut health, unveiling the remarkable complexities of the gut-brain axis. This article delves into the multifaceted world of pet nutrition and gut health, empowering you with the knowledge to make informed choices for your furry companions.

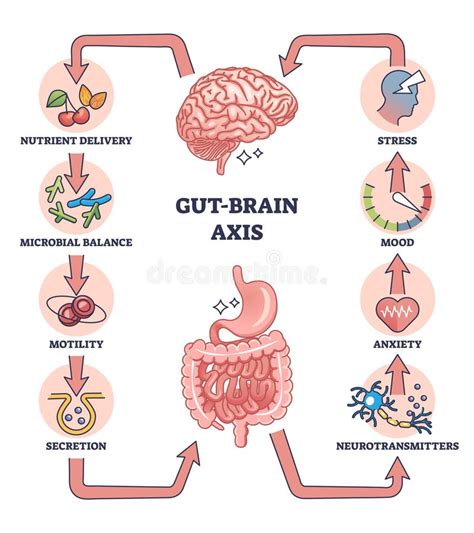
The Gut-Brain Axis: A Vital Connection
The gut-brain axis is a bidirectional communication pathway between the gastrointestinal tract and the central nervous system. It consists of intricate neural, hormonal, and immune connections that enable bidirectional communication between the gut and the brain.
The gut microbiota, composed of trillions of microorganisms residing in the digestive tract, plays a crucial role in the gut-brain axis. These microorganisms produce various molecules that can influence brain function, mood, and behavior. Conversely, the brain can also influence the gut microbiota through the release of neuropeptides and hormones.
Impact of Gut Health on Pet Health
Maintaining a healthy gut microbiome is essential for overall pet health. A well-balanced gut microbiome can:
- Support the immune system by producing antimicrobial substances and modulating immune responses
- Enhance digestion and absorption of nutrients by breaking down complex compounds and producing enzymes
- Reduce inflammation by inhibiting the growth of harmful bacteria and producing anti-inflammatory molecules
- Promote neurological health by regulating neurotransmitter production and influencing brain function
Factors Affecting Pet Gut Health
Numerous factors can impact the health and composition of the pet gut microbiome, including:
- Diet The type and quality of food your pet consumes directly influences the gut microbiota. A balanced diet rich in prebiotics, probiotics, and fiber supports a healthy gut microbiome.
- Lifestyle Exercise, stress levels, and exposure to environmental toxins can all affect gut health.
- Health status Certain diseases and illnesses can disrupt the gut microbiome and lead to dysbiosis, an imbalance in the microbial community.
Prebiotics, Probiotics, and Fiber: Essential Nutrients for Gut Health
- Prebiotics are non-digestible food ingredients that selectively promote the growth of beneficial bacteria in the gut. Examples of prebiotics include inulin, fructooligosaccharides (FOS), and galactooligosaccharides (GOS).
- Probiotics are live microorganisms that, when consumed in adequate amounts, confer health benefits to the host. Common probiotics include Lactobacillus, Bifidobacterium, and Streptococcus thermophilus.
- Fiber is an essential dietary component that supports gut health by providing sustenance for beneficial bacteria and promoting regular bowel movements.
Symptoms of Gut Health Issues in Pets
Recognizing the signs of gut health issues in pets is crucial for prompt intervention and treatment. Common symptoms include:
- Diarrhea
- Constipation
- Vomiting
- Flatulence
- Abdominal pain
- Weight loss
- Dull coat
- Lethargy
Diagnosing Gut Health Issues in Pets
Veterinarians diagnose gut health issues in pets through a combination of clinical examination, fecal analysis, and specialized tests, including:
- Fecal microbiota analysis This test analyzes the composition and diversity of the gut microbiota.
- Bloodwork Certain blood tests can indicate inflammation or other abnormalities related to gut health.
- Biopsy In some cases, a biopsy of the intestinal tissue may be necessary to rule out underlying diseases.
Treatment of Gut Health Issues in Pets
The treatment of gut health issues in pets often involves a multimodal approach, including:
- Dietary modifications Adjusting the pet’s diet to include prebiotics, probiotics, and fiber can support gut health recovery.
- Medications Antibiotics may be prescribed to treat bacterial infections, while anti-inflammatory medications can alleviate inflammation.
- Probiotics Probiotic supplements can help restore balance to the gut microbiota.
- Fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) In severe cases, FMT, the transfer of healthy fecal microbiota from a donor animal, may be used to repopulate the pet’s gut with beneficial bacteria.
Strategies for Maintaining Gut Health in Pets
Maintaining optimal gut health in pets requires a holistic approach that incorporates the following strategies:
- Provide a balanced diet Feed your pet a high-quality diet rich in prebiotics, probiotics, and fiber.
- Encourage regular exercise Exercise promotes digestive function and reduces stress levels, both of which benefit gut health.
- Minimize stress Stress can disrupt gut health; provide your pet with a calm and comfortable environment.
- Limit exposure to environmental toxins Keep your pet away from toxins such as pesticides, herbicides, and heavy metals.
- Regular veterinary check-ups Regular check-ups allow your veterinarian to monitor your pet’s gut health and provide timely interventions as needed.
Conclusion
The relationship between pet nutrition and gut health is an intricate and dynamic one. By understanding the role of the gut-brain axis and the importance of a healthy gut microbiome, we can make informed choices to support our pets’ optimal well-being. Through proper nutrition, lifestyle modifications, and veterinary care, we can ensure our furry companions enjoy a long, happy, and healthy life.